What is Niacin?
Niacin is a water soluble Vitamin b3. Another form of Vitamin B3 is Nicotinamide. Niacin is a pyridine carboxylic acid, also known as Nicotinic acid, Vitamin B3, Vitamin PP, 3-Pyridinecarboxylic acid, widely used as food and feed additive, also used as vasodilator. Niacin is essential to human life and the deficiency can result in a wide variety of side effects.
Niacin is an immediate precursor of NAD and NADP which plays an important role in animal energy utilization, synthesis and catabolism of fats, proteins and carbohydrates.
Niacin or Nicotinic acid Properties
Molecular Formula: C6H5NO2
Appearance: white crystaline powder or granular, free flowing, sparingly soluble. It is seldom affected by acids, bases,oxygen, heavy metal ions, light and heat.
Molecular Weight:M-123.11
Chemical structure: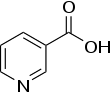
Is Niacin or Nicotinic acid water soluble?
It is soluble in water. Solubility 18 g L−1
Where does Niacin or Nicotinic acid comes from?
Niacin is found in a variety of whole and processed foods, including fortified packaged foods, meat from various animal sources, seafood and spices.
Difference between Niacin and Nicotinic acid?
Niacin and Nicotinic acid are same. Another name for niacin: Nicotinic acid, Pyridine-3-carboxylic acid
Niacin or Nicotinic acid Function
Niacin or Nicotinic acid is converted to niacinamide in the human body, involved in lipid metabolism, oxidation in tissue respiration and anaerobic decomposition for carbohydrate oxidation. It’s mainly used in medicine, food and feed additives field.
In animal feed additives, its main functions are: to prevent skin lesions and digestive diseases; to promote animal growth, improve egg production and hatching rate, to ensure feather growth; to treat mucosal inflammation and ulceration; Prevent the livestock and poultry from perosis.
In medicine and food additives, and its main functions are: to prevent of skin lesions and digestive diseases; to promote participation in the body of material and energy metabolism, to promote human growth and development; to treat a variety of mucosal inflammation and ulcers with other drugs; Strong vasodilator effect, to improve the blood supply to the body function, feature favorable effect on cerebral thrombosis, coronary heart disease, hyperlipidemia and so on; to treat nicotinic acid, nicotinamide deficiency caused by its long-term medicament of isonicotinic acid hydrazine and analogs. As a pharmaceutical intermediate, Nicotinic acid is used for production of isoniazid, niacinamide, nikethamide and inositol nicotinate.
How does Niacin or Nicotinic acid work?
Niacin is absorbed by the body when dissolved in water and taken by mouth. It is converted to niacinamide if taken in amounts greater than what is needed by the body.
Niacin is required for the proper function of fats and sugars in the body and to maintain healthy cells. At high doses, niacin might help people with heart disease because of its beneficial effects on clotting. It may also improve levels of a certain type of fat called triglycerides in the blood.
Deficiency of Niacin or Nicotinic acid in the body
Long term niacin deficiency results in a disease called “pellagra.” Niacin is involved in DNA repair as well, so a shortage of this vitamin is not something you want. Low dietary amounts of niacin have even been associated with various forms of cancer.
The most common symptoms of niacin deficiency involve the skin, the digestive system, and the nervous system. The symptoms of pellagra are commonly referred to as the three “Ds”: sun-sensitive dermatitis, diarrhea, and dementia. A fourth “D,” death, occurs if pellagra is left untreated. In the skin, a thick, scaly, darkly pigmented rash develops symmetrically in areas exposed to sunlight. In fact, the word “pellagra” comes from “pelle agra,” the Italian phrase for rough skin. Symptoms related to the digestive system include inflammation of the mouth and tongue (“bright red tongue”), vomiting, constipation, abdominal pain, and ultimately, diarrhea. Gastrointestinal disorders and diarrhea contribute to the ongoing malnourishment of the patients. Neurologic symptoms include headache, apathy, fatigue, depression, disorientation, and memory loss and are more consistent with delirium than with the historically described dementia. Disease presentations vary in appearance since the classic triad rarely presents in its entirety. The absence of dermatitis, for example, is known as pellagra sine pellagra.
Reference: http://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/vitamins/niacin
Why do we need Niacin or Nicotinic acid?
One of the most important reasons why we all need niacin is that all of the B vitamins help to turn our food into energy. Niacin, in particular, helps increase “good” cholesterol and lower “bad” cholesterol. Niacin can also help to balance sex hormones.
Niacin is a direct precursor of coenzyme I and coenzyme II and plays an important role in animal and human energy utilization and the synthesis and breakdown of fats, proteins and carbohydrates.
Nicotinic acid is essential for normal function of the nervous system and the maintenance of healthy skin and mucous membranes. Without it, the body cannot convert food into glucose to produce energy.
Niacin or Nicotinic acid effect on triglycerides
Vitamin B3, better known as niacin, is also an effective at lowering triglycerides. Triglycerides are risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Serum triglyceride levels are affected by age, sex, and diet. Increased serum triglycerides can be seen in familial hypertriglyceridemia, eating large amounts of triglycerides and secondary to certain diseases such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, nephrotic syndrome and pancreatitis, atherosclerosis, and glycogen storage. Accumulation and other diseases.
The benefits of niacin on triglyceride levels are related to the vitamin’s effects on the liver. Niacin actually reduces the VLDL and LDL producing abilities of the organ. VLDL cholesterol is comprised primarily of triglycerides, which is why the benefits of niacin are so valuable for this purpose.
Does Niacin or Nicotinic acid lower blood pressure?
Nicotinic acid (niacin) is a well-established treatment for dyslipidaemia – an important cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factor. However, niacin may also reduce blood pressure (BP), which is another important CVD risk factor.
Reference: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2705821/
Niacin or Nicotinic acid skin benefits
speed up cell metabolism and cell turnover (a process that slows down with age), revealing younger skin. It also helps heal wounds, repair sun damage and hyperpigmentation, and strengthen the skin barrier, making skin better able to retain moisture.
Niacin is also known to have a beneficial effect on skin cancer. Studies have shown that it can prevent premalignant cells from becoming malignant. And talking about anti-aging, niacin does play its part. One study showed that topical niacinamide helped reduce fine lines and wrinkles and other issues with skin elasticity concerned with aging.
How does Niacin or Nicotinic acid reduce cholesterol
niacin in very large doses can improve cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart attacks. In fact, when niacin’s beneficial effect was discovered in 1955, it became the first treatment for high cholesterol.
The main goal of cholesterol treatment is to lower bad cholesterol. niacin has the advantage of raising good cholesterol. It also lowers triglycerides, fats in the blood that can increase the risk of heart disease.
Is Niacin or Nicotinic acid good for weight loss
As niacin can break down fat and get rid of toxins stored in fat cells, so some hold the opinion it can help weight loss.
Niacin or Nicotinic acid use
Niacin or Nicotinic acid is used in dietary supplementation and also used to improve cardiovascular health and maintain healthy cholesterol levels. Today, many types of food (rice, cereals, milk, etc.) are enriched with Vitamin B3. Many breakfast drinks, soft and sport drinks contain a cocktail of vitamins. Niacin or Nicotinic acid is used in these formulations to cover approximately one third to one half of the daily requirement. Dietetic food include infant formulas, slimming diets, special foods for athletes, medical feeding ingredients (enteral nutrition products). In general, foods for special dietetic use are fortified with all essential vitamins, minerals and trace elements to prevent deficiencies. Niacin or Nicotinic acid is very stable as a pure substance, in vitamin premixes and in processes such as baking. It is an essential vitamin needed for protein, carbohydrate and fat metabolism.
Uses and Applications in Human Nutrition
Food and Beverage Fortification
- Flour enrichment
- Grain enrichment
- Cereal enrichment
- Energy drinks
- Meal replacements
Health and Beauty Products
- Cosmetics and toiletries
- Anti-aging and acne skin care
- Hair care
- Face and body moisturizers
- Toothpaste
Therapeutic Nutritional Ingredient
- Infant formulas
- Dietary supplements
- Multivitamins
- Nutritional beverages
- Adult nutrition
Uses and Applications in Animal Nutrition
Vitamin B3 is essential to health of animal nutrition. Supplementation with vitamin B3 as niacin (nicotinic acid) or niacinamide (nicotinamide) helps animals metabolize feed to increase nutrient absorption and conversion to energy. As a leading manufacturer and supplier of the vitamin B3 and a leading supplier of vitamin B3 nutrition products for animal, human, and pharmaceutical applications. We have much extensive experience in the science of vitamin B3 supplementation into animal feed.
Feed Grade Niacin or Nicotinic acid: The amount and bioavailability of vitamins in animal feed is generally insufficient to fully nourish livestock. Therefore, supplementing with vitamin B3 Niacin or Nicotinic acid is essential. Deficiencies in vitamin B3 can be devastating to animals, resulting in decreased feed intake, retarded growth, weakness, and digestive tract disorders. In poultry the symptoms of malnutrition can include poor feathering, perosis, and black tongue.
Niacin-deficient pigs may develop ulcerative necrotic lesions in the gastro-intestinal tract, resulting in diarrhea and bacterial infection. Providing monogastric livestock with added vitamin B3Niacin or Nicotinic acid protects and promotes health of mucous membranes, central nervous system, skin, bones and joints. The following examples support the use of vitamin B3 supplementation for animal nutrition.
- Animal Health: In ruminants, increased levels of vitamin B3 improve digestive tract health.
- Growth and Feed Efficiency: Pigs fed with dietary vitamin B3 show increased gain-to-feed and pork quality; Vitamin B3 supplementation in chickens improves weight gain and feed utilization. Performance: In early-lactating dairy cows, dietary Niacin increases milk production via increased amounts of coenzymes NAD and NADP.
Why is Niacin or Nicotinic acid used in food?
Niacin and niacinamide are forms of Vitamin B3. Vitamin B3 is found in many foods including yeast, meat, fish, milk, eggs, green vegetables, beans, and cereal grains.Niacin and niacinamide are also found in many vitamin B complex supplements with other B vitamins. Niacin is used for high cholesterol.
Niacin or Nicotinic acid food source
Niacin is found in a variety of foods. There are many Paleo friendly foods which contain this B vitamin, especially in great abundance. The top 4 foods, in fact, are all Paleo mainstays: tuna, chicken, pork and liver. Beef, mushrooms and avocado all contain niacin as well. In fact, it is a good idea to try and obtain all of your niacin via food. As you will see, it becomes harder to supplement with this vitamin than one would think.
Recommended Dietary Dosage of Niacin and Niacinamide
| Age, year | Weight, kg | Niacin, mg/d | |
| Infants | 0-0.5 | 6 | 5 |
| 0.5-1 | 9 | 6 | |
| Children | 1-3 | 13 | 9 |
| 4-6 | 20 | 12 | |
| Men | 11-14 | 45 | 17 |
| 15-18 | 66 | 20 | |
| 19-24 | 72 | 19 | |
| 25-50 | 79 | 19 | |
| > 51 | 77 | 15 | |
| Women | 11-14 | 46 | 15 |
| 15-18 | 55 | 15 | |
| 19-24 | 58 | 15 | |
| 25-50 | 63 | 15 | |
| > 51 | 65 | 13 | |
| Pregnant women | 17 | ||
| Nursing mothers | 20 |
Examples:
Today, many types of food (rice, cereals, milk, etc.) are enriched with vitamins. Many breakfast drinks, soft and sport drinks contain a cocktail of vitamins. Niacin and Niacinamide are used in these formulations to cover approximately one third to one half of the daily requirement.
Dietetic food like infant formulas, slimming diets, special foods for athletes, medical feeding ingredients (enteral nutrition products). In general, foods for special dietetic use are fortified with all essential vitamins, minerals and trace elements to prevent deficiencies.
A classic example of food fortification is the addition of B vitamins (including niacin/niacinamide) to wheat flour.
Flour Enrichment
Application of specific premixes will result in a flour which meets the requirements of the respective authorities.
| Required | mg per kg flour | |
| minimum | maximum | |
| Vitamin B1 | 4.0 | 5.0 |
| Vitamin B2 | 2.4 | 3.0 |
| Niacin/Niacinamide | 32.0 | 40.0 |
| Iron (II) | 26.0 | 33.0 |
Breakfast Drink
| content in 100 g | |
| Niacinamide | 18 mg |
| Vitamin B1 | 1.4 mg |
| Vitamin B2 | 1.6 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 2 mg |
| Pantothenic acid | 6 mg |
| Vitamin B12 | 1 microgram |
| Vitamin C | 60 mg |
| Folic acid | 0.2 mg |
| Biotin | 0.15 mg |
| Vitamin A | 0.8 mg |
| Vitamin D | 5 microgram |
| Vitamin E | 10 mg |
| Vitamin K | 0.1 mg |
Multivitamin Tablets
To ensure nutritional equivalence or to compensate for naturally occurring variations in nutrient levels or to compensate for a higher demand, multivitamin tablets with varying formulations are offered by the industry.
Typical Formulation of 1 Tablet (2.0g)
| Vitamin | active content per tablet | % RDA |
| Niacinamide | 0.9 mg | 50 % |
| Vitamin C | 30.0 mg | 50 % |
| Pantothenic acid (Ca salt) | 3.0 mg | 50 % |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.7 mg | 50 % |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.8 mg | 50 % |
| Vitamin B6 | 1.0 mg | 50 % |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.5 microgram | 50 % |
| Folic acid | 0.1 mg | 50 % |
| Biotin | 0.075 mg | 50 % |
| Vitamin E | 5.0 mg | 50 % |
Is Niacin or Nicotinic acid bad for you?
Commonly Niacin or Nicotinic acid is a considered safe vitamin, but there are several side effects that is bad for your health. The common side effects are as follows:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea: niacin may cause diarrhea
- Skin reactions, rashes
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Allergic reactions: Niacin supplements can cause allergies because some contain histamines, chemicals substances that can trigger allergic symptoms to be released
- Heart problems: High doses of niacin may increase the risk of irregular heartbeats
- Diabetes: Niacin and niacinamide might increase blood sugar. People with diabetes who take niacin or niacinamide should check their blood sugar carefully.
- Worsened gallbladder or liver disease symptoms
- Aggravated gout symptoms.
- Low blood pressure
- Stomach or intestinal ulcers
- Problems after surgery controlling blood sugar levels
Reference: https://draxe.com/niacin-side-effects/
Niacin or Nicotinic acid Market
Vitamin B3 is one of the eight B-complex vitamins and plays an essential role in many physiological functions. The body constantly uses vitamin B3 to support metabolism of carbohydrates and proteins, blood circulation, and the functioning of the nervous system. Most people do not consume or synthesize enough dietary vitamin B3 to support adequate health wellness. A chronic lack of vitamin B3 can cause pellagra, a vitamin deficiency disease.
Over the years, Niacin has remained well-recognized for treating individuals with high cholesterols. In countries with malnutrition being one of the major concerns, regulatory bodies are setting up guidelines for food fortification including edible oil, salt, milk, wheat flour, and rice. The use of niacin and niacinamide in majority of these food products is one of the aspects of food fortification in these countries, in order to prevent vitamin B3 deficiency.
Deficiency of vitamin B3 leads to development of pellagra. Although pellagra is less prevalent in developed regions on the back of food fortification programs, certain countries in Africa such as Ethiopia, Zaire, and Malawi have a slew of reported cases related to pellagra.
A health-conscious trend is fostering across the developed regions, with consumer awareness concerning health benefits of various dietary supplements such as niacin and niacinamide witnessing a rise. In addition, utilization if niacin in the cosmetics, particularly in skin care cosmetics, is gaining huge attraction owing to its ability of protecting skin cells from UV rays.
As projected by Future Market Insights (FMI) in its new research analysis, the global market for niacin and niacinamide will ride on a steady CAGR during the forecast period (2017-2026). Global sales of niacin & niacinamide are estimated to garner roughly US$ 1,500 Mn revenues by 2026-end.
Reference: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/niacin-and-niacinamide-market-global-industry-analysis-2012—2016–opportunity-assessment-2017—2026-300598863.html
Niacin or Nicotinic acid /Nicotinamide Price trend
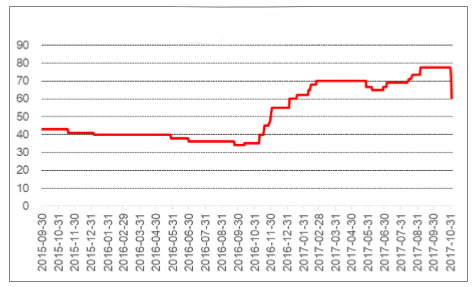
Vitamin B3 Niacin or Nicotinamide is involved in lipid metabolism in the body, the process of tissue respiration and the anaerobic decomposition of carbohydrates. It is mainly used in the field of feed additives (67%), medical cosmetics (20%) and food (13%).
Supply side: Vitamin B3 is highly competitive and oversupply. In 2015, global production of niacinamide/nicotinic acid was about 65,000 tons, global demand was about 58,000 tons, and China’s demand was about 11199 tons. In 2015, China produced 21,700 tons, exported 11,600 tons, imported 2,000 tons, domestic supply totaled 12,100 tons and consumed 11,100 tons.
In 2016, the global output was about 24,900 tons, the export was 11,500 tons, the import was 1200 tons, the domestic supply totaled about 14,600 tons, and the total domestic demand was about 11,600 tons. In the past two years, the nicotinamide/nicotinic acid market has been fiercely competitive.
Price: The limited use of Paraquat inhibited VB3 intermediate product output, and the increase in intermediate prices has driven VB3 prices to rise.
The intermediate product of vitamin B3 is pyridine and 3-picoline as concomitant products. Pyridine is mainly used for the production of paraquat. Since 2012, the country has begun to restrict or prohibit paraquat. The national regulations of 2016 will stop the sale and use of paraquat aqueous solution in China since the 1st of July 2016. R & D of paraquat alternative formulations Bottleneck, there are no more new dosage forms in the country through the review, still only two types of formulations “pass”, the development of paraquat alternative formulations is very difficult. Upstream pyridine production is therefore limited, resulting in a decline in 3-methylpyridine production and an increase in the cost of vitamin B3. At the end of September 2016, the price of niacinamide began to rise from the bottom of 25 yuan/kg, and was recently maintained at 77.5 yuan/kg.
Niacin or Nicotinic acid Specification
Feed grade, assay ≥99.0%
Food grade, assay ≥99.5%
Recommended Niacin or Nicotinic acid dosage in livestock and aquatic animals
Recommended dosage in the formula of feed for Poultry & livestock & aquatic compound feed recommended amount:20-100g per ton.
Recommended dosage in the formula feed for cow during pregnancy and lactation period recommended amount:300g per ton
Packaging & Storage
Packaging: 25kg/carton or bag.
Storage: Store in dry, cool and dark places.
Shelf life: 24 months. Once the original cartons have been opened, please use the goods within a short period.
Niacin or Nicotinic acid manufacturers
Vitamin B3 Niacin or Nicotinic acid is an essential vitamin needed for protein, carbohydrate and fat metabolism.Niacin or Nicotinic acid is vitamin of the Vitamin-B group, the precursor in the synthesis of the pyridine coenzymes NAD and NADP involved in cell metabolism. Vitamin B3 can be found in various foods, but its bioavailability depends greatly on the source. China production occupies the large part in the world.
China is the big food and feed grade Niacin or Nicotinic acid manufacturers and export country in the world.
There are several Niacin or Nicotinic acid manufacturers in China and abroad, as you know, the price of China suppliers can be better than abroad manufacturers. We have worked with China top manufacturer for years, we would like to recommend our selected Niacin or Nicotinic acid manufacturers to you if you would like to save your purchasing cost with the same quality compared with abroad manufacturers. Niacin or Nicotinic acid Samples are available if you need it for further test.
Where to buy Niacin or Nicotinic acid?
You can buy food or feed grade Niacin or Nicotinic acid from us. We’re committed to the quality and safety of our ingredients. We know that our customers expect us to use only the highest quality food additives & ingredients with better price, and we do everything we can to satisfy those expectations.
If you have any other questions, please email us through: info@foodsweeteners.com