What is Gellan Gum E418?
Gellan gum E418 is a kind of microbial extra cellular polysaccharide. It is functioned as a thickening, gelling agent and stabilizing agent. Gellan gum has been used in the food, medicine(e.g. soft or hard capsule), cosmetic, chemical industry, etc. Gellan gum has two types: low acyl Gellan gum and high acyl Gellan gum. It is suitable for vegetarian or for vegan diets.
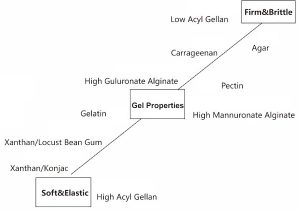
Low acyl gellan gum products form firm, non-elastic, brittle gels, whereas high acyl gellan gum forms soft, very elastic, non-brittle gels. Varying the ratios of the two forms of gellan produces a wide variety of textures.
The uniqueness of gellan gum is the ability to suspend while contributing minimal viscosity via the formation of a uniquely functioning fluid gel solution with a weak gel structure.
Other name for Gellan Gum: Gelling agent E418, E418 food additive
Gellan gum E418 structure
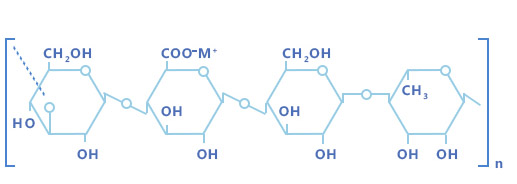
Gellan gum is a high molecular linear polysaccharide, which is formed by repeated polymerization of basic units composed of 4 monosaccharide molecules. The basic units are two glucose residues linked by 1,3- and 1,4- linkages, one glucuronic acid residue linked by 1,3-, and one rhamnose residue linked by 1,4- linkages composition.
Among them, glucuronic acid can be neutralized by potassium, sodium, calcium, and magnesium into a mixed salt. And natural gellan gum contains O-acyl (glycerol acyl and acetyl). Natural or high acyl gellan gum can form high elasticity and low hardness gel. High acyl gellan gum removes O-acyl groups by alkali treatment to produce low-acyl gellan gum, which can then be filtered to obtain a purified low-acyl gellan gum, which is a commercial gellan gum with a relative molecular weight of about 500,000.
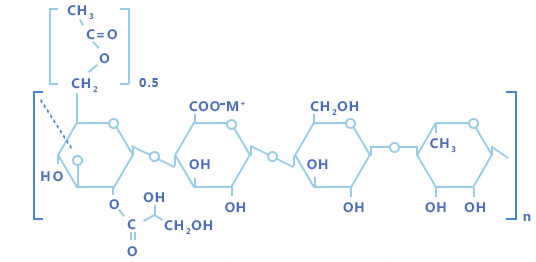
In low acyl gellan gum, the acyl groups are removed completely. The acyl groups have a profound influence on gel characteristics. The high acyl form produces soft, elastic, non-brittle gels, whereas the low acyl form produces firm, non-elastic, brittle gels.
| Comparison of High Acyl and Low Acyl Gellan Gum | ||
| High Acyl Gellan Gum | Low Acyl Gellan Gum | |
| Molecular Weight | 1 – 2×106 Daltons | 2 – 3×105 Daltons(2) |
| Solubility | Hot water | Hot or cold water |
| Set Temperature | 70º – 80ºC (158º – 176ºF) | 30º – 50ºC (86º – 122ºF) |
| Thermoreversibility | Thermo-reversible | Heat stable |
E418 Gellan gum manufacturing process
What is E418 gellan gum derived from?
Gellan gum is similar to xanthan gum as it is also produced by bacterial fermentation. Gellan gum is a polysaccharide produced by fermentation of a pure culture of Sphingomonas elodea. The composition and structure of native gellan gum produced by commercial fermentation is identical to the nature-based occurring polysaccharide formed by Sphingomonas elodea on plants of Lily pad varieties.
Since the presence of the acetyl group will seriously affect its gel properties, it is necessary to add potassium hydroxide to the resulting mash. Alkaline to remove acetyl and glycerol groups, low acetyl gellan gum has been achieved. It is then heated, filtered and alcoholized with isopropanol to give a deacetylated clear gellan gum
E418 Gellan gum properties
Gellan gum powder is beige in color, no special taste and odor, will decompose about 150°C.
With properties of good heat and acid resistance, high stability to the enzyme. It is insoluble in non-polar organic solvents, also insoluble in cold water, but Gellan gum disperses in water with slight stirring. It dissolves in a transparent solution upon heating. After cooling, Gellan gum forms a transparent and firm gel. It is soluble in hot deionized water or a low ionic strength solution that is present in the integrator. The aqueous solution is neutral.
In the presence of cations, gellan gum forms a hard, brittle gel when cooled after heating. Its hardness is proportional to the gellan gum concentration and produces maximum gel strength at lower divalent cation concentrations. Gellan gum is generally used in amounts of 0.05% to form gels (usually in amounts of 0.1% to 0.3%). The formed gel is rich in water, has a good flavor release, and has a mouth-feeling texture. The gelling temperature of gellan gum is in the range of 30-45°C, and the melting temperature of the gel can be lower or higher than 100°C, depending on conditions such as cation type and concentration. The addition of xanthan gum, locust bean gum, to gellan gum can reduce its gel hardness and increase its elasticity.
- Effective at very low concentrations, ensuring no flavor masking
- Gels on cooling
- Manufactured by fermentation, so its quality is consistent and supply is reliable
- Giving a wide range of textures from brittle to elastic
Pure gellan gum is a compound salt, insoluble in cold water, but can directly disperse in deionized water under stirring, increase the concentration of cations in water, such as water with medium hardness (equivalent to CaCO3, 180mg/kg). Helps its dispersion in water. However, Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, and K+ ions (such as hard water) can prevent the dispersed gellan gum from being heated and hydrated. The higher the concentration of cations, the less hydration cannot be achieved even when heated to boiling.
In the already dispersed water, adding a small amount of chelating agent (such as sodium citrate, sodium hexametaphosphate) can make the dispersed gellan gum hydrate even in high hardness water, as long as the amount of the added chelating agent and Ca2+ The content is such that it is even soluble in cold water. The hot uniform hydrated gel solution can be directly gelled after cooling, but it needs to be added after being added with cation, and the hardness and modulus of the gel can be increased to the maximum with the increase of cation concentration, but the concentration exceeds a certain limit. , which will reduce the hardness and modulus of the gel, and the optimal concentration of monovalent cations and divalent cations is not the same.
Gel Formation
Gellan gum solutions form gels on cooling. The setting temperature will depend on the grade of gellan gum, which cations are present and their concentration, and the presence of other dissolved solids. In the absence of added cations, low acyl gellan gum gels set at around 25ºC (77ºF), where high acyl sets at around 65ºC (149ºF). With added calcium or sodium ions, the setting temperature increases.
Low acyl gellan gum typically forms gels in the range of 30 – 50ºC (86 – 122ºF), while high acyl gellan gum normally forms gels at around 70ºC (158ºF). Gellan gum sets very quickly, as soon as the setting temperature has been reached. This is known as “snap” setting. High acyl gellan gum forms a gel simply on cooling.
Low acyl gellan gum, however, requires cations, acid, soluble solids or some combination of these additives. Divalent cations such as calcium and magnesium are the most effective for gel formation, but sodium and potassium will also work to form a gel. To optimize gel properties, it is sometimes necessary to add extra cations. Optimization is often accomplished by adding a soluble calcium salt. To avoid localized gelation, the cations are best added when the solution is hot. The solution then gels on cooling.
PH
The pH of most foods is between 4.0 and 8.0. Gelling gels in this pH range have almost no change in gel strength with changes in pH. When gellan gum is used in food ph from 4.0-8.0, pH change can be ignored.
The gellan gum gel formed by divalent cations, when at a pH of less than 3.5 or greater than 8.5, the gel strength decreases rapidly; the gel formed by monovalent cations has slight fluctuations in the pH between 3.5-1 L.5. However, the gel strength of divalent cations is much greater than that of monovalent cations in gels formed at the same gel concentration.
Thermo-reversible
Gels In most practical situations, gels made with low acyl gellan gum are not thermally reversible. Most gels of low acyl gellan gum are retort or bake-stable. Gels made with high acyl gellan gum will soften with heating, and will melt with prolonged heating. The greater the concentration of ions, the higher the melting temperature.
Gel Texture
One of the most important features of a gelling agent is the texture it provides. Low acyl gellan gum forms hard and brittle gels. High acyl gellan gum forms soft and elastic gels.
Blends of Low Acyl and High Acyl Gellan Gum
Low acyl gellan gum gels have a firm, brittle texture. Adding a high acyl gellan gum reduces the brittleness. By varying the ratio of these two forms of gellan gum, a wide variety of textures can be obtained. Blends of low acyl and high acyl gellan gum can match the texture of other hydrocolloids. By varying the ratio of low acyl and high acyl gellan gums it is possible to obtain textures close to those of carrageenan and gelatin gels.
Compare with others Gels
Low acyl gellan gum is a brittle gel, very sensitive to shear force, with clear taste. Compared with other food gels, gellan gum has obvious advantages, and it’s now gradually replacing agar agar and carrageenan in the food industry. Following picture shows the properties of gellan gum in comparison with other gels.
E418 Gellan gum use and application
Due to the excellent gel properties of gellan gum, it has gradually replaced the use of agar and carrageenan.
Gellan gum is widely used in foods such as puddings, jellies, sugars, beverages, dairy products, jam products, bread fillings, surface smootheners, candy, sugar coatings, seasonings, and the like. It is also used in non-food industry, such as microbial culture medium, slow release of drugs, toothpaste and so on.
| In Food | beverage, sweets, jam, jelly, gels, synthetic food, pet food, sugar coating, frosting, dairy and baked products |
|---|---|
| In Medicine | eye drops, soft or hard capsule, microcapsules |
| In Cosmetics | skincare products, perfume |
| In Daily Chemical | coating, tackiness agent, toothpaste, car balm, air freshener |
| In Agriculture | fertilizer gels |
| Others | microorganism, plant culture medium, photosensitive film |
Gellan gum can enhance the hardness, elasticity and viscosity of noodle products. It also improves taste, inhibits hot water swelling, reduces cross-section and reduces turbidity of soups. It can also be added to biscuits to improve biscuits, make biscuits have a good degree of looseness; gellan gum as a stabilizer applied to ice cream can improve shape retention; used in cakes, cheese cakes, with moisturizing, preservation and conformal effect;
Gellan gum used in candy can provide products with superior structure and texture, and shorten the time of formation of starch jelly candy; Also can be used to replace pectin for the preparation of jams and jellies, can also be used for cakes and fruit pie filling;
In meat products and vegetables, during the processing, adding gellan gum will give it a refreshing taste, and it will play a good role in making up for the lack of product taste. Gellan gum can be used together with other hydrocolloid for gel in pet food; it can be mixed with sucrose, sodium citrate, slow-dissolving acid (fatty acid, adipic acid, etc.) into dry material, added into boiling water, and made into extremely transparent hot water dessert gel, the flavor release is good after the it is broken quickly in mouth ; it can replace pectin to make jam. Starch can also be combined with starch or partially substituted, with cakes and tart fillings.
E418 Gellan gum Safety
Gellan gum appears in the USP/NF (first Supple-ment April 1, 2004 USP 27/NF 22).
Gellan gum is an approved FDA food additive as per 21 CFR 172.665. Gellan gum appears as E418 in the European Community Directive EC/95/2 in Annex 1. Gellan gum is listed in the Food Chemicals Codex, Canada Food and Drug Act (Division 16, Table IV, G.2), Japanese Specifications and Standards for Food Additives (JSSFA).
Both the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) and the European Community Scientific Committee for Food have given gellan gum an Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) of “not specified”. Meaning toxicity at any amount has not been reported. Excessive intake may cause side effects like abdominal bloating, excessive gas (flatulence), loose stools or diarrhea.
E418 Gellan gum market
Gellan gum market forecast
The global gellan gum market is expected to witness significant growth over the forecast period owing to its high demand from food & beverage applications. It is used as a substitute or alternative to hydrocolloids in beverages and dairy products, thus propelling its demand in food processing industry. High growth of Food and beverage industry across major economies of the world including the U.S., Europe, India and China owing to rising consumer dependency on packaged food products, is expected to drive product growth over the next eight years.
The product finds its application in several industries including cosmetic, food, personal care, industrial cleaning, and pharmaceutical. Growing demand for the product as oil content stabilizer in personal care items including face lotions, creams, face washes and masks is expected to propel industry growth over the projected period.
The ability of gellan gum to retain the elasticity and structuring of molecules thereby preventing ingredients change during temperature changes is expected to drive growth. The product can be used as an alternative to locust bean gum, xanthan gum and guar gum as binder and stabilizer in food products. Furthermore, it can also be used as an alternative to gelatin in vegan food products and helps in preventing melting of ingredients in desserts and ice-creams. However, high penetration rates of these products in end-use applications is expected to hamper growth for gellan gum market over the projected period.
Gellan gum E418 manufacturers
China is the big Gellan gum manufacturers and export country in the world.
There are severalGellan gum manufacturers in China and abroad, as you know, the price of China suppliers can be better than abroad manufacturers. We have worked with China top manufacturer for years, we would like to recommend our selected Gellan gum suppliers to you if you would like to save your purchasing cost with the same quality compared with abroad manufacturers. Gellan gum Samples are available if you need it for further test after accept the price.
Gellan gum E418 price
As you know, there are two types of Low acyl gellan gum and High acyl gellan gum the market. The price is based on different types. Please contact us if you need a price idea.
Where to buy Gellan gum E418?
All the products listed in our website are from the manufacturers we have worked together for many years. The professional working experience backup our confidence to their quality. We can supply Gellan gum E418 for many Specifications and we can be your suppliers in China.
By using the appropriate Gellan gum E418 types in your food, the formulator can create suitable products with good gelling agent, thickener and stabilizer.
We’re committed to the quality and safety of our ingredients. We know that our customers expect us to use only the highest quality and healthiest ingredients available, and we do everything we can to satisfy those expectations. We feel confident in our choice to choose top Gellan gum E418 manufacturer brand.
If you have any other questions, please email us through: info@foodsweeteners.com
FAQ
E418 Gellan gum vs E407 carrageenan?
Gellan gum has a good taste than Carrageenan.
Carrageenan needs much time to gel after cool while Gellan gum gel can form fast.
Is Gellan gum gluten free?
Yes, Gellan gum is gluten free
Is E418 gellan gum the same as E407 carrageenan?
No, they’re different, Gellan gum is derived from fermentation while Carrageenan comes from seaweed.
Is E418 gellan gum suitable for vegetarians?
Yes, Gellan gum is suitable for vegetarian or for vegan diets.
E418 Gellan gum vs E415 xanthan gum?
Gellan gum is similar to xanthan gum as it is also produced by bacterial fermentation.
Gellan gum can form gel while xanthan cannot.